Slim pickings for Vodafone shareholders
Delayed IPO has meant depressed valuation; company says market conditions not right
Katya Naidu Mumbai Vodafone Plc and its ex-shareholders have suffered due to the delay in an Initial Public Offer (IPO) of its Indian unit.
Ex-shareholders such as Piramal Enterprises, Analjit Singh and IDFC got much less than if there had been an IPO when the parent company bought back its stake from them.
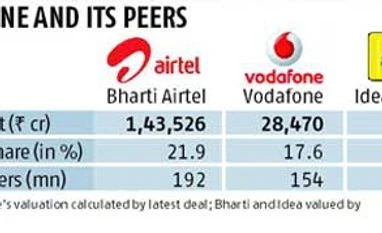
Vodafone has valued its Indian unit at a mere Rs 28,470 crore, based on what it paid for its stake. The current valuation is much less than the Rs 57,000 crore that Vodafone paid Hutch in 2007 to buy 67 per cent stake in the company.
Jagannadham Thunuguntla, chief strategist at SMC Global, says Vodafone's valuation would be closer to Bharti Airtel (market cap of Rs 143,526 crore), even as the latter has other businesses such as operations of its African entity, Zain, and other businesses like direct-to-home, etc. “Also, Bharti Airtel has debt, which Vodafone does not have. We should consider debt as well when we do a peer-to-peer equity valuation,” he said.
With the latest buyout, Vodafone Plc has valued its Indian entity at half that of Idea Cellular, the third largest company in the segment. Idea's market capitalisation is Rs 56,741 crore. “Idea is much smaller than Vodafone as a company. Vodafone is a market leader in some circles; in others, it holds the second position,” said Mahantesh Marilinga, senior research analyst at Finquest.
Bharti Airtel has 192 million subscribers, with a 21.9 per cent market share; Vodafone has 154 million subscribers, with 17.6 per cent market share. Idea has 126 million, with 14.3 per cent market share.
An IPO for Vodafone has been initiated many times but could not go through for various reasons. One is the multiple tax cases on the parent company. The government is claiming Rs 11,200 crore as tax for its 2007 deal to buy 67 per cent stake in Hutchison Essar. It has two more cases over transfer pricing issues, being fought in the courts.
Vodafone Plc says the condition of the markets is the reason behind the delay. Experts do agree. “In the past four years, there have been no IPOs. Also, the telecom sector is not doing well, as more than 90 per cent of the population has mobiles and there is not much growth from here. It all depends on how much revenue you can get from the existing telecom base,” said Thunuguntla.
Marilinga agrees, saying there would be no improvement in the valuations of telecom companies until they start making money from their 3G (third generation services) businesses. “It has started (data growth) but is yet to attain scale,” he said. In spite of the drawbacks of the sector, a company such as Vodafone could have listed and commanded valuations with its peers, a loss to those who sold out.
“Vodafone held 64 per cent directly but indirectly it held the stake of its shareholders. It (parent company) could have decided the valuation,” said Marilinga. On the other hand, Vodafone's earlier shareholder, Essar, had managed to get a premium from its stake.
In 2011, after much negotiation, Essar agreed to sell its 33 per cent stake to Vodafone for $5.46 billion.
)

)