Monsoon 2015 ends with 14% shortfall
Worst performance since 2009, rains poor in almost 40% of area
Sanjeeb Mukherjee New Delhi This year's southwest monsoon has ended with a rain shortfall of 14 per cent, the worst since 2009. This has stoked fear of a climatic drought in at least 30 per cent of the geographical area, though the impact on agriculture could be checked on the back of a late surge. The rains were normal in around 55 per cent of the country.
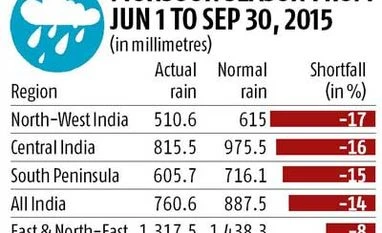
India Meteorological Department (IMD) says from June 1 to September 30, the country got 760.6 mm of rainfall, as against a normal average of 887.5 mm. The department had predicted that the rains would be 12 per cent less than normal; the deficit was wider. Technically, the southwest monsoon ended on Wednesday. However, it might take another week to 10 days before showers stop across the country. IMD says withdrawal of the southwest monsoon is complete over parts of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat.
There were signs of a revival towards the season's end in some parts. This could leave some moisture in the soil, helping the coming rabi. The monsoon from September 17 to 23 was 68 per cent more than normal, IMD data showed.
Despite, the late resurgence, almost 40 per cent of the country had deficient rain in the entire season, with parts of UP, Maharashtra, the northwest parts and Odisha staring at drought-like conditions. “We are satisfied that our Long Range Forecast have turned out as per our prediction. This was for the first time that we made a prediction of more than 10 per cent deficiency,” IMD Director General Laxman Singh Rathore said.
Northwest India had a deficiency of 17 per cent, followed by 16 per cent in central India, 15 per cent in the southern peninsula and eight per cent in east and northeast India. June saw 16 per cent excess rain but July had a deficiency of 16 per cent. This grew to 22 and 24 per cent for August and September, respectively.
Foodgrain production is projected to drop by 1.8 per cent to 124.05 million tonnes in the kharif (summer) season. The output was 126.31 mt in last year's kharif.
Year 2015 was the first back-to-back drought for India in three decades, and only the fourth in more than a century.
As on September 23, the 91 major reservoirs monitored by the Central Water Commission were filled to the extent of only 62 per cent of their combined 253.388 billion cubic metre capacity.
)
)